Setting a NEW standard in softness
Softness has become as essential as absorbency in modern hygiene care. Leading brands must achieve both—luxurious comfort and uncompromised functionality.
Line characteristics:
Typical web weights: 15 to 100 gsm
Fibers: PP/PE, PET/Co-PET bicomponent fibers
Output: more than 14,000 tons/year (depending on fiber type, web weight and working width)
Typical end products: top and back sheet and ADL (acquisition/distribution layer) in diapers
Common working width: 3300 mm, 3800 mm, 4200 mm
The world's only 0.6-denier ATB technology for ultra-soft hygiene products.
Setting a new benchmark in Air-Through Bonding (ATB) technology, we offer the world’s only processing solution capable of precisely manufacturing 0.6 denier ultra-fine sheath-core bicomponent microfibers. This enables the production of lightweight, dual-layer webs with unmatched softness, loft and skin compatibility at industry-leading production speeds and availability rates.
These webs give an ultra-soft, fluffy touch to both the top and back sheets, while the underlying acquisition distribution layer (ADL) features a lofty, open-pore structure that ensures rapid liquid aquisition and uniform distribution. They are the ideal choice for premium baby diapers and other modern absorbent hygiene products - delivering overall comfort and high-performance functionality.

Ultra-fine fiber, ultra-Exceptional.
The world's only proven card capability of processing 0.6 denier ultra-fine fibers to achieve a homogeneous web with the lowest nep count - delivering exceptional quality.

Widest usable web width in the market - Up to 4% more material utilization
With a 3.8 m roller card at 130 m/min, 24 gsm, and 7,200 hours of annual production, the widest usable web width adds up to more than 200 tons of extra output compared to production lines including other nonwoven cards.

Trützschler Clean Concept - High-speed production, fewer stops
Saving 2 hours of maintenance per week can add up to 70 tons of output per year (24 gsm, 130 m/min, 50 weeks).
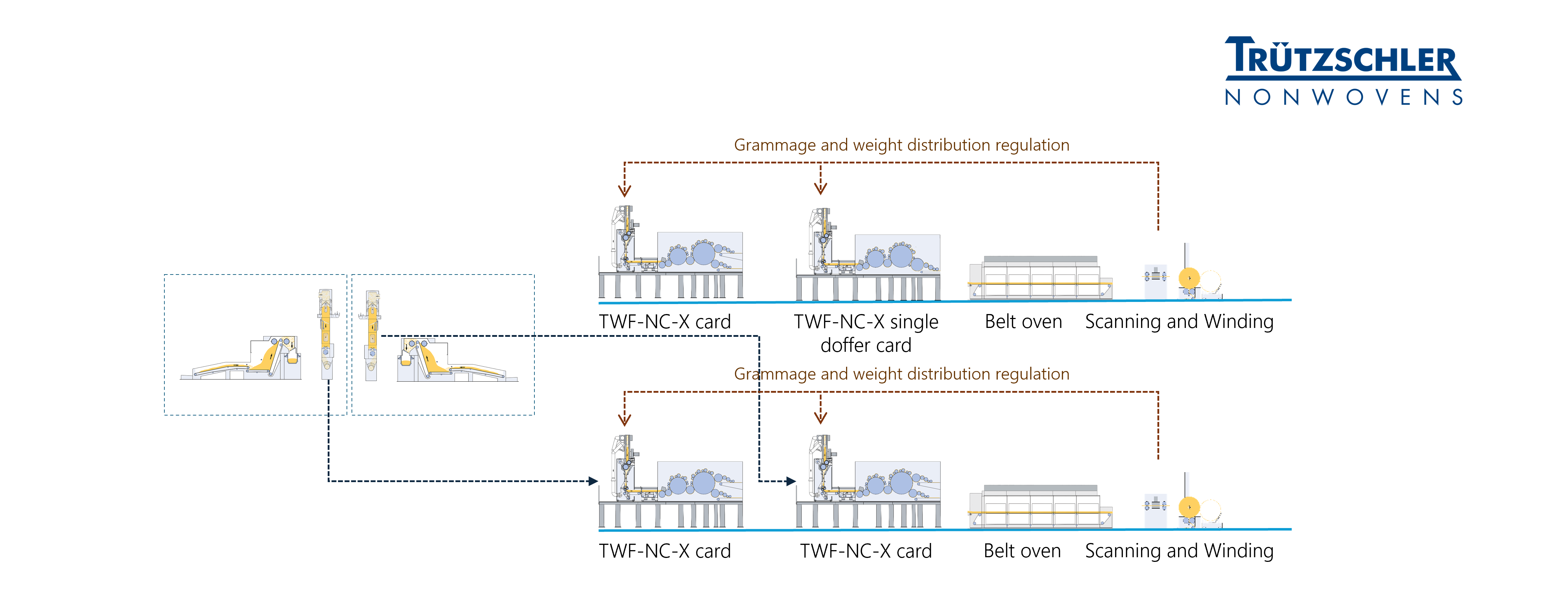
T-BLEND fiber preparation and NC-X nonwoven card ensure web quality - the foundation of premium nonwovens.
Sheath/core bicomponent fibers below 1 denier form the foundation of ultra-soft, lightweight premium nonwovens produced on ATB lines. Their extremely fine structure makes them fragile and prone to entanglement – which is why precise preparation and controlled processing are essential for stable, homogeneous webs.
To achieve this, the T-BLEND fiber preparation system applies gentle fiber opening and ensures continuous, uniform material flow from the bale opener to the web former.
The NC-X nonwoven card offers configurations , specifically developed for hygiene applications, gently processes ultra-fine fibers at every carding point. Its precisely engineered internal structure ensures smooth airflow and prevents air swirls, resulting in optimal fiber parallelization, homogenous, minimal nep count and consistently high-loft webs.
Trützschler Nonwovens Air-Through Bonding (ATB) line.

Achieving success with over 90% market share
In China, we have achieved outstanding success with our ATB solutions – holding more than 90% market share and delivering nearly 100 nonwoven cards. Thanks to our unique web structure and superior softness, Trützschler Nonwovens is the preferred partner for premium topsheet and backsheet materials, trusted by the world’s leading hygiene brands.
A flexible line for air-through bonded nonwovens
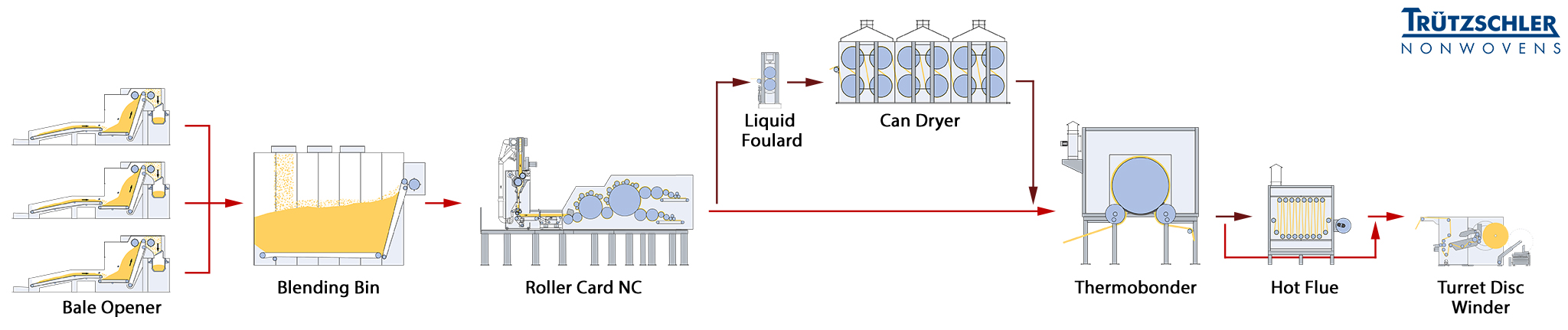
Chemical bonding with foulards
Nonwovens in absorbent hygiene products can also be produced using chemical bonding. Chemical or binder bonding takes place by applying binders to the unbonded web. When drying the liquid or foam-based chemical binders glue the surrounding fibers together.
Key components are, on the one hand, the applicator, which apply the binding liquid or foam evenly to the surface of the web. Several drying components follow. First, the web transits a can dryer, then an Omega dryer and finally a hot flue, a dwelling compartment.